A vegan diet is one of the best things to follow in terms of excellent health and longevity. Although a plant-based diet has numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges like the lack of vitamins in your body. Here, we discuss several vitamin deficiencies that occur and how to overcome them.
What Happens To Your Body When You Experience Vitamin Deficiency?
Here are some of the symptoms:
- Extreme tiredness and weakness
- Poor digestion
- Developmental delays in children
- Nausea
- Balance and memory problems
ASSUAGED VITAMIN RICH FOODS GUIDE
Top 6 Vitamin Deficiencies In Vegans
When being on an entirely plant-based diet, some nutrients are challenging to get from plants or to get them in an adequate amount. Below is a list of the top 6 vitamins that vegans are most often deficient in:
- Iron
- Calcium
- Vitamin B-12
- Vitamin D
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Zinc
Recommended Daily Dosages
- Iron -8.7 mg a day for men over 18. 14.8 mg a day for women aged 19 to 50. 8.7 mg a day for women over 50.
- Calcium -2,500 mg a day for adults 19 to 50. For those 51 and older, the limit is 2,000 mg a day.
- Vitamin B -1.2 - 2.4 micrograms a day.
- Vitamin D - an average daily intake of 10 to 20 micrograms.
- Omega-3 fatty acids -minimum of 250 –500 mg a day.
- Zinc - 8 mg a day for women and 11 mg a day for men.
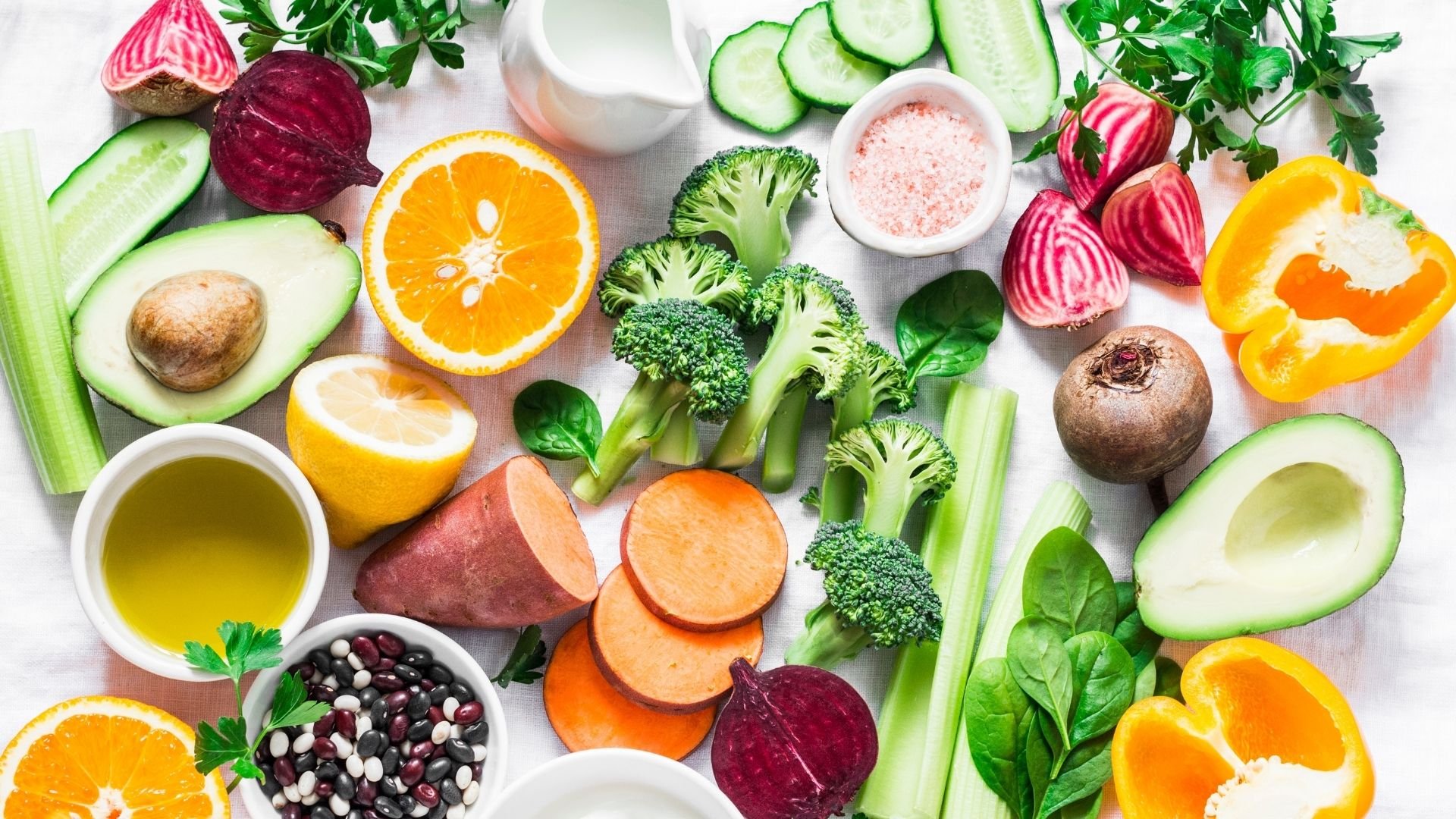

How Can A Vegan Avoid Deficiencies?
Below are some alternative food sources that can be consumed to compensate for the lack of these vitamins:
- Iron - pulses (beans, lentils, and peas), greens, nuts, dried fruits, cereals that are rich in iron.
- Calcium - soy milk, oat milk, almonds, sesame seeds, and tahini.
- Vitamin B-12 - yeast extract (marmite), soy products, and cereals that are rich in vitamin B-12.
- Vitamin D - fortified soy milk, mushrooms, fortified orange juice, and fortified rice milk (sunshine isn’t a food, but it is an excellent source of vitamin D).
- Omega-3 fatty acids -chia seeds, flax seeds, walnuts, and hemp seeds.
- Zinc -beans, legumes, and whole grains.
** IMPORTANT NOTE: Soak the beans/legumes before cooking.**
As you can see, there are several alternatives to fulfill the intake requirements of the most common vitamins that we may lack while following a vegan diet.
Choosing a healthy plant-based and vegan diet is most beneficial when it comes to:
-
Higher levels of energy;
-
Improved sleep;
-
Aids in energy and overall happiness;
-
Provides a sense of comfort and relief;
-
Could prevent major diseases such as obesity and diabetes;
-
Accomplish weight-loss and management; and
-
Improves mental and cognitive functioning.
There are really no excuses not to try healthier habits in your everyday life. If you are a man or woman looking for specific benefits of adopting healthier habits or just want to know about the general healing properties of herbs. Please remember to comment or post any health questions, or contact us directly!

Resources:
-
Barrington, Kate. "The Top 5 Nutrient Deficiencies on a Plant Based Diet." July 5 2018. Web. <https://www.naturespath.com/en-us/blog/the-top-5-deficiencies-on-a-plant-based-diet/>.
-
Raman, Ryan. "The Best Vegan Sources of Vitamin D." April 28 2018. Web. <https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-d-from-sun>.
-
Rizzo, Gianluca et al. “Vitamin B12 among Vegetarians: Status, Assessment and Supplementation.” Nutrients vol. 8,12 767. 29 Nov. 2016, doi:10.3390/nu8120767
- "Vegetarian and vegan diets Q&A." August 2 2018. Web. <https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/vegetarian-and-vegan-diets-q-and-a/>.